SAP provides large amounts of data that needs to be managed in a structured way. This can be achieved through the use of SAP Master Data Management. The main purpose of this article is to introduce and explain the concept of SAP Master Data Management (MDM) and its usage with the help of an example project. We will also discuss some important features, benefits, challenges, and limitations that are associated with it.
This brief guide will show you how to build a comprehensive and robust SAP master data solution that can be used by your ERP and CRM applications. And it will also introduce some things you should look out for when trying to do so, including enabling customers, external partners, applications as well as course management
Table of Contents
What is SAP Master Data
SAP Master data is the core data that serves as the foundation for any transaction. SAP Master Data is critical because it provides business context by providing models of data that can be used to guide business processes. This ensures that SAP master data is consistent across analytical and transactional systems. Information that is of high value to is used by an organization repeatedly throughout numerous business processes
- SAP Master Data provides information about main business entities: Suppliers, Customers, and other business partners Products, charts of accounts, and employees
- SAP Master Data content is valuable information that an organization can reuse across multiple business processes.
- SAP Master Data is important because it provides business context by providing concrete data models for business processes.
- Making sure that SAP master data is consistent ensures that master information is consistent across Systems for analytical and transactional processing
What is the Purpose of SAP Master Data
The data is scattered across a variety of systems. We aren’t sure which data is correct. Making reports is a difficult task. Inconsistent SAP Master data could cause:
- Repetitive Data entry
- Inconsistency arises as a result of data from various transactions.
- Incorrect data resulting in unsatisfied customers, rework, or revenue loss
- A large amount of training is required in educating users on entering data on various screens.
- Inefficient use of time
Use of SAP Master Data
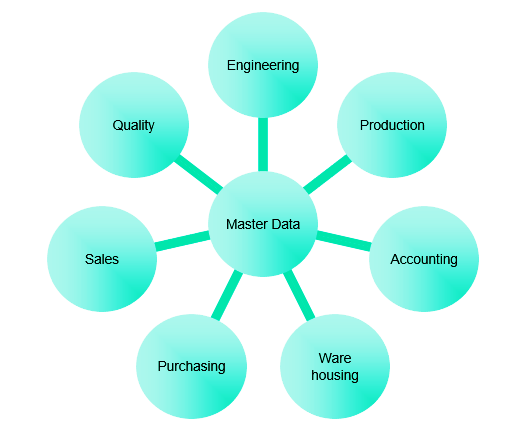
- SAP Master are stored centrally (shared between departments)
- which is then processed to remove redundant data.
- SAP Master Data aids in transaction validation and quick user entry.
- A single-time creation of data that is not often modified. The data can be changed only once. the data that is incrementally required to be kept.

SAP Master Data Type
There are various types of SAP Masters in the system. The primary master data that are stored in SAP include the customer’s master and material masters as well as the customer’s material record. Other data that are based on condition-based methods include:
- Customer Master Data
- Material Master Data
- Customer Material info Record
- Transactional Master Data

Customer Master Data
The customer master contains all relevant information required to process inquiries or quotations, place an order, deliver an order, invoice, and pay the customer. The Customer Masters may be assigned numbers automatically based on the Configuration Settings. Most customers share the same general Data, Sales Area, and Master Data. They can also be extended to a variety of different sales areas or Company codes. SAP will ask you to select the appropriate one when you enter an order.
The basic information in the master customer record includes the customer’s name and address, which are kept at the client level. Accounting information (reconciliation account) is included at the company level, and sales level data include shipping, sales, and billing-related fields. The customer account group can be used to control field selection for the master customer record.
Customer Account Group:
An account group is a classification of customer master records, The customer account group controls the following:
- What fields of the master record of this are mandatory or not required?
- The customer’s number range is determined by the Account ID (external as well as internal)
- If it’s a one-time Customer account /regulars customer
- The default value for the pricing procedure indicator
Menu Path: IMG >>Logistics General>>Business Partner >>Customers >>Control

In the screen below, you can configure field selections based on account group as needed for your business. However, the procedure for configuring it in accordance with the company code or transaction is the same. You can use the field selection feature to specify which fields are mandatory, optional, visible, or hidden for each account group.
Menupaths:IMG>>Logistics General>> Business Partners>> Customers >> Control>>Define account groups and field selection for customer

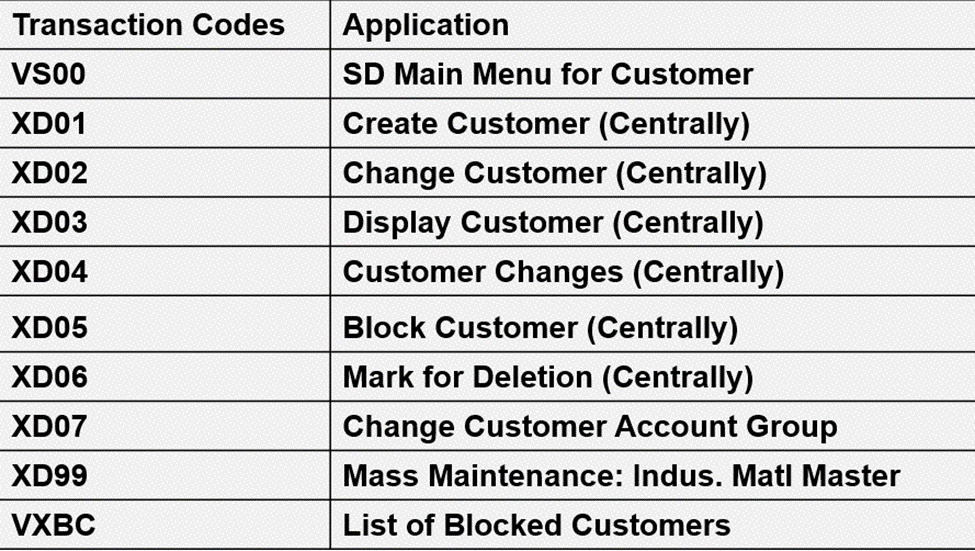
In SAP, what is the Tcode for customer master?
Material Master
Material Master provides information about every material that an organization purchases or manufactures and stores, as well as sells. The information contained within the master material is necessary for the following tasks:
- In purchasing for order
- In Inventory Management for the posting of goods post-movement postings and physical inventory
- Invoice Verification to ensure posting of invoices
- For Sales and Distribution to assist with the processing of sales orders
- the Production Planning and Control for material requirements, planning, and work schedules

Material Type:
Material Type in Material Master determines the range of numbers as well as the views and screen layout. The views in the material master are kept at an org level at a certain point.
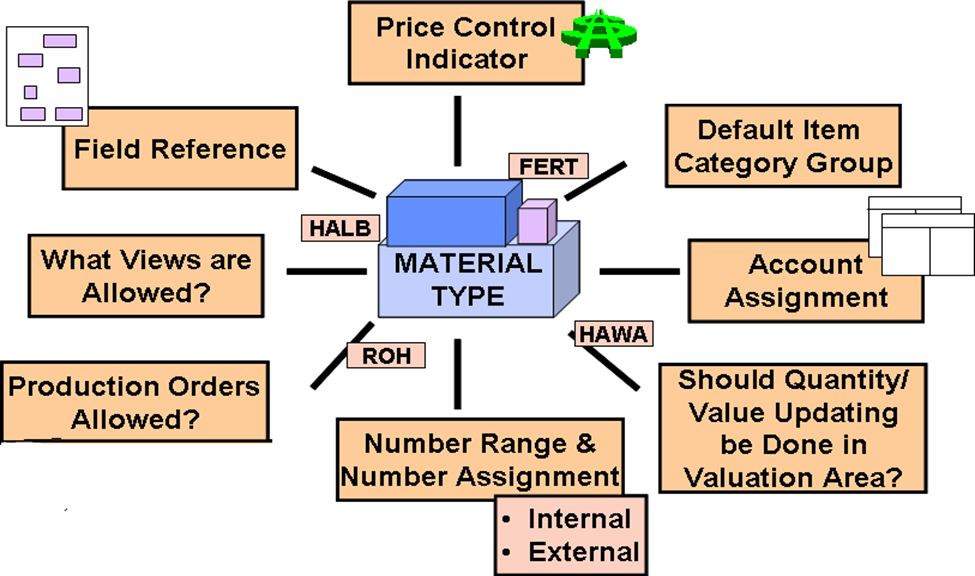
Configure material types: IMG >>Logistics General>>Material Master>>Basic Settings >>Material Types >>Define Attributes for Material types
- The basic data is stored at the client level. This means that all the company codes that are part of the client will have identical values under the basic data of material.
- The purchasing view is kept at the plant level. It is possible to maintain different values in the purchase view of materials for different plant.
- MRP view is kept at Plant Level, Storage Location
- Material master also contains additional information that includes material text, and conversion of different units of measurement.
- The same material is utilized in different departments Therefore, the material is used by different Departments. numerous views.
- Material Master is the main view (Basic Data MRP and Purch. org) as well as Additional Views (UOM Text, UOM, etc.)
- The Material Master Material Master some views are maintained at the Client Level while others are maintained at an Org level like the Plant Level.
- The information contained included in Material Masters is either descriptive (name size, name, etc.)) or it can be used to control specific functions (material grp or the procurement keys).
- Materials that share the same basic characteristics are put together and assigned to a type of material.
- It allows users to manage different materials in a consistent way in line with the needs of your company.
- The type of material determines the properties of the material and performs important functions of control.
When creating a master material document, the owner needs to make sure that the item is assigned to the type of material.
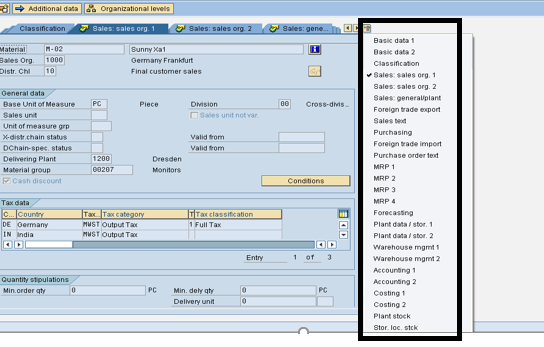
Material Master – Configuration
Menu path Logistics General >>Material Master>>Settings for Key fields.
- Here you can define Material Groups, Division,
- Material Statuses, Storage and Temperature Conditions, ABC Indicators, etc

Material Master numbering: Follow the menu below to alter the format of your company’s support format. You can also customize the format of your numbering of the material master.
IMG >>Logistics General >> Material Master>>Logistics General >>Material Master >>Basic settings>>Define Output format of Material Numbers

It is only feasible to reset or set (cancel) that indicator (Lexicographical) in the event that the numeric material number has not been utilized within the system. It is possible to define, a combination of the user and screen sequences and the levels of organization that is set when the user edits, creates, or displays a master material record.

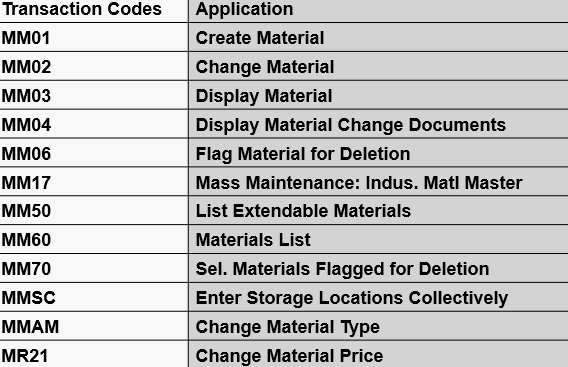
What is the transaction code for material master?
Customer-Material Info Record
What is Customer-Material Info Record in SAP SD?
Customer Material Info Record is basically used to store the information about how a particular material is referred by a customer. Customer-Material Info Record has priority over Customer Master & Material master records. The information specific to the material of the customer is more important than general data. Consequently, when different delivery information is recorded in the customer master record as well as in the customer-material-related information record, the customer-material-specific information record will take precedence.

For instance, during the process of delivery Plant selection, for example, the CM Info Record is accessed first. The system copies the material’s identifier and details about the delivery of the product into the purchase order.
The material information that is specified for each customer is recorded in the customer-specific information record. It consists of:
- A specific material number to the customer (up 30 to 35 characters) and a description
- Delivery information, including tolerances and the plant
- You can maintain the customer-material information record by maintaining the relevant customer master record (Environment>>Cust-Material info) or
- Separately using the below menu path
Customer-Material Info Record– Configuration
Logistics>> SD >>Master Data>>Information System>>Agreements>> List Customer-Material-info
You can input products by entering the specific customer materials number into the “Customer material” field on the screen for order overview, Ordering Party
Transactional Master Data
Transactional data pertains to the organization’s transactions and includes data captured, for example, when a product is sold or purchased. Customer, product, pricing, output, and supplier data are examples of master data used in various transactions.
Condition Master
Condition Master data is saved in the form of a Condition record (information about prices, text partners, substitute materials, etc.) during the process of processing sales orders the system employs the condition method to find the data. Once the setup is completed, you will maintain the condition records which allow you to keep and retrieve the information in the system.
The Configuration for Condition Technique functions by following a method:
- Define the condition types for each element
- The condition tables permit you to store and retrieve the condition data for the various types of conditions.
- Determine the access sequences that allow the system to search for authentic condition records.
- Group conditions and determine their order for pricing processes.
Condition Master – Example

- The pricing components used in your daily pricing processes such as surcharges, price discounts, freight charges, and taxes are identified by the R/3 software in terms of the condition types.
- When a sales order is entered The system calculates prices automatically, by calculating the gross price, removing all discounts applicable, and adding any additional charges like freight or sales tax.
- Based on the pricing guidelines of your business You may be able to alter the prices of sales orders manually during processing. It is possible, for example, you can create or change certain discounts during the time frame.It is possible to make changes to certain discounts within a specific time frame.
Condition Master – Output
Output types represent different types of output within SAP. Output types represent different forms of output in the SAP system. Examples of the kinds of documents that are utilized in sales and distribution processing are order confirmation invoices, freight lists, and other invoices. You can choose Extras like Output a Header or Print Preview, which summarizes the documents for sales.
You can print output documents multiple times. This is useful in the event that you find that there is a technical issue or another when printing an output document for the first time.

Condition Master– Texts
Texts are derived from master records found in the documents for distribution and sales when you have selected the proper settings. It is possible to integrate text from standard sources into distribution and sales documents.

Texts can be copied directly from an existing reference document of distribution and sales into a different document that is a sales and distribution (e.g. from an inquiry about the sales order, or from order to delivery ).
- Text copying text is able to be made language-dependent in the event that it is required.
- You can alter the copied text
- In the Sales Document, text can be kept as Header text as well as Item Text
Condition-Based Transactional Master Data
Here is other Condition-based transactional master data :
Pricing: condition technique is a search strategy to find the right condition among the various prices ing information contained inside condition records condition type. The process of determining the right price was controlled by the various configurations.
Text Processing: In the context of a business partnership, it is vital that business partners exchange data across the entire logistics chain. For distribution and sales, the exchange of information is supported by text in master documents and records. It is possible to keep these documents for Material Masters or Customers or create them in a way that they can be utilized more flexibly. Example: Sales Notes to customers, shipping instructions for Deliveries
Output Determination Output Determination component has output functions for shipping, sales transportation, billing, and sales to assist you in managing the sales transactions of your customers and within your own company. Output types can be used to represent different types of outputs in SAP. SAP system. The types of output used in the sales and distribution processing are shipping lists, order confirmations, and invoices.
Free Goods: If you provide customers free goods You can set up an automated free goods determination. The system will automatically generate the free item on the sale purchase. The item is provided free for all to use. In the case of free items that are inclusive the primary item is reduced automatically by the number of free goods. In the case of exclusive free items, the amount of the primary item remains the same.
Material Determination The standard ordering process customers request is the exact product that is then shipped. However, there are instances when you’d like to replace the order with another alternative, such as an item that is packaged for Christmas or coupons or samples for free.
Cross-Selling: Retailers often utilize cross-selling to boost sales. If a client purchases an item via phone, the person taking the order may suggest other items that the client could purchase. For example, if a customer is looking to buy a VCR it is possible to recommend buying blank tapes, or for phones with cellular capabilities, you could suggest a leather case for carrying.
Materials Listing & Exclusion Materials listing, as well as exclusion, allow you to determine which products specific customers can or cannot purchase. For instance, if making a listing of materials for a specific client that customer can only purchase items from the list. It is also possible to create a master list of material exclusions for a specific customer. This way, the customer will not be able to buy excluded items from you.
You Might Also Like the below articles