This article will briefly outline SAP Customer Relationship Management (SAP CRM ) and some of the primary SAP CRM module features in the following article. We will also provide details about how a company can use SAP CRM to define its goals, its advantages, and more information about the structure of SAP CRM modules. you will find out more about the core SAP CRM domains (i.e., sales, marketing, and service) using SAP CRM software used by different industries.
Table of Contents
Introduction of SAP CRM
CRM stands for Customer Relationship Management. CRM is a widely accepted, widely implemented method of managing and nurturing your company’s interactions with clients and potential sales customers.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is crucial for organizational success, enabling businesses to provide seamless experiences, predict customer needs, and deliver personalized service. SAP CRM, a leading provider, integrates seamlessly with other systems, offering tools for managing all aspects of customer relationships, including sales, marketing, service, and social engagement. With advanced capabilities and flexible architecture, SAP CRM is helping businesses improve efficiency, effectiveness, and customer satisfaction.
SAP CRM allows an organization to be a relationship-based integrated, information-driven, processes-oriented, real-time and efficient customer-centric, and customer-responsive enterprise.
What is CRM Module?
SAP CRM is a submodule within the SAP ERP application; SAP Customer Relationship (SAP CRM) is a software that delivers top-of-the-line sales, marketing and service capabilities. It uses technology to manage and automate the business process and make it synchronized, including sales-related activities and those related to customer service, marketing, and technical assistance. The main goal is to identify, attract and acquire new customers, cultivate and keep those that the business already has, bring previous customers back to their fold, and cut down on customer service and marketing expenses.
With its support for customer-facing business processes across various interaction platforms, SAP CRM enables organizations to concentrate on strategies to drive customer-driven growth and differentiate their company from competitors by offering a better customer experience.

CRM Advantages
SAP CRM Benefits for Organizations Competitive Advantages
- Increased Revenue
- Potential to lower opertional Costs
SAP CRM Benefits for Customers
SAP CRM offers significant benefits to businesses, including improved customer satisfaction, increased sales efficiency, enhanced marketing effectiveness, and better service delivery. Its tools enable effective understanding and response to customer needs, streamline sales processes, and provide insights for targeted marketing strategies, ultimately fostering stronger customer relationships for long-term business success.
- Better and Personalized service
- Continuous interaction across channels as well as contact points
- Superior features for sales, marketing and service
- Analysis of extensive depth as a basis to make a decision
- Integration is seamless seamlessly SAP Business Suite solutions and other applications.
CRM Overview – Key Functionalities
In everyday business, different departments such as Marketing, Sales and Service communicate regularly and directly with customers.
From a computer point of view, these employees must have the support they require to complete their tasks efficiently and in a customer-focused manner.
Introduction to Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
SAP CRM is the leading system in the world for web-based front-office solutions that support marketing, sales, and customer service. The massive popularity of SAP is due to the fact it is SAP CRM software is extensive yet also able to be customized to meet the requirements of every company. Many companies prefer off-the-shelf solutions such as SAP because they are customizable and can meet the needs of any business in any sector. SAP can be implemented on various hardware platforms, providing the same complete and integrated capabilities, as well as the flexibility to address each company’s specific requirements and make sure that it is independent of particular technologies used in the organization. SAP provides a process-oriented view of the larger enterprise.
CRM System applications offer the framework to implement the most effective practices for dealing with customers. It provides a standard platform for interaction and communication with customers. The application for CRM System applications helps in improving the customer’s responsiveness. It also offers a comprehensive overview of the complete Customer Life Cycle.
A CRM System such as SAP CRM will provide this versatility and completeness since the components comprise every business object, data object and user interface (UI) application utilized by the entire system. There are also additional support subsystems to help control and secure this program’s operation daily.Off-the-shelf software, particularly business-wide solutions like CRM systems, are seen as the most effective approach to facing the software shortage of the
CRM Systems, like ERPs, have extended the notion of reusability and functionality that a system can provide. For example, SAP CRM was based on the fundamental commonality that is found in the workings of businesses that are part of an industry. SAP created a library that could be reused for the most commonly used processes within a specific field. The only thing SAP CRM users had to do was select from this library the procedures required by their organization.
From the project’s cost and effort that was crucial for the creation and implementation of the standard SDLC , CRM reduced the effort and price of the project to a level that was only associated with the implementation stage in the SDLC.
In this way, CRM Systems ended the supporting and secondary function that IT has played over the last couple of decades. But the fundamental aspect of IS has undergone an entirely new change. Implementing a CRM system within an organization is no longer an issue of technology; it’s a business issue. CRM Systems have been the precursors to an evolution in an enterprise’s IS/IT function.
Architecture
SAP CRM provides a complete solution that covers every point of contact at which your company communicates with its customer. It’s part of the SAP Business Suite that provides essential functions for marketing, sales, and services across various ways of communication (i.e., IC, Web Channel, Field Application, and SAP Enterprise Portal).
SAP CRM functions as a core component that includes CRM servers and is integrated with it through the SAP ERP backend system. In most scenarios for business, the master data is complete from the SAP ERP system and then is then replicated to SAP CRM for later use by customers. SAP CRM Analytics allows you to examine the master and transactional information that you have entered into your SAP CRM software. When you connect the system to SAP Supply Chain Management (SAP SCM) solutions, SAP CRM can execute the available to Promise (ATP) checks and report results on locations and products in relation to the availability of the product.
The SAP CRM ecosystem includes SAP CRM Application Server (AS) ABAP and SAP CRM AS Java, allowing you to run various business procedures. If you price any of your transactions, SAP CRM uses the Internet Pricing and Configurator (IPC) to charge products. The IPC function to price is now integrated into the Virtual Machine Container (VMC), which is an integral part of the SAP CRM’s CRM deployment. To use VMC, it is optional to set up SAP CRM AS Java separately. SAP CRM AS Java component individually because the VMC is part of SAP CRM AS ABAP. SAP CRM AS ABAP component. To deploy Web Channel, you must install the SAP CRM AS Java component. Web Channel, you need to install the SAP CRM AS Java component.
What CRM is Used for
SAP CRM is a crucial business process across your business and forms the base for a distinctive customer experience. SAP CRM focuses on customers as well as your business’s expansion, simplifies your entire business process, and reacts more quickly to changes within the market.
Let’s look at the main features and applications that SAP CRM uses to get over any challenges related to serving customers.

Image by SAP
What are the main modules of CRM?
The three pillars of SAP CRM are marketing, sales, and service. We’ll look at these in more detail in the following Below sections.
SAP CRM Marketing
Marketing in SAP CRM assists an organization in attracting new customers as well as retaining existing customers. It stimulates customer demand with the help of the following functions that facilitate direct mail and call centre services email, web, and field sales.

Marketing Resource Management (MRM)
MRM aids organizations in managing their marketing budgets, marketing resources campaigns, personnel, and budgets efficiently. Since businesses alter their marketing strategies in response to market trends, they have in a position to shift budgets or funds that have been allocated to individual product promotion. This can be done with the help of the native Funds Management in SAP CRM to move funds to meet market demands and shifts. A Marketing plan serves as a foundation for a budget that will be based on your marketing requirements generally, while the campaigns focus on specific actions that are executed to meet your needs in marketing.
Segmentation as well as List Management
Segmentation and List Management enables organizations to separate customers targeted for specific customer attributes and send out campaigns to these particular customers.for Example if you want target specifiy age /gender or geographies for marketing .
Campaign Management
A company can utilize Campaign Management to execute its campaigns through various communication channels, including outbound and inbound media (i.e. phone or mail, email, SMS, web, fax, etc.). In general, when a business is creating its marketing strategy, it makes an account for the campaign and assigns it. This is the way to link the execution of the marketing plan as well as the movements that are transferred to the strategy. The target groups are designated to the campaigns in order to carry out the promotions for the products.
Lead Management
Finding the most precise lead sources is essential to achieving organizational growth and new businesses. Lead Management is a function in SAP CRM that enables the business to collect leads and maintain the charges. Once the information has been recognized, the company determines whether the leader is cold or hot once the tips are transformed into sales opportunities and orders.
Trade Promotion Management (TPM)
Trade promotion is an agreement between the seller and the client to provide the product for an agreed-upon time for a specified amount and/or price. Trade promotion can boost brand capital and brand recognition, and market share. SAP CRM provides this capability and assists you in linking the marketing plan with the trade promotion, and also integrates the trade promotion into Claims and Funds Management.
Analytics in marketing
SAP CRM provides a marketing analytics feature that lets an organization look at vital information about its business’s marketing function and makes decisions based on that information. These analytics comprise SAP Predictive Analytics measuring and reports and forecasting, customer analytics, planning optimization and refinement, and product analysis.

Image by SAP
SAP CRM Sales
Sales is the main SAP CRM feature that enables firms to sell their items or services to their customers and then records the sales as transactions. The term “sales” is a simple concept: selling the product and then pushing it through the logistics process and into invoicing.SAP CRM helps provide a complete overview of the entire sales process, starting with the contract, quote, and continuing to the creation of sales orders as well as delivery and billing details. SAP CRM Sales provides the following essential functions:

Opportunity Management
The sales process within SAP CRM begins with Opportunity Management and ends with Sales Order Management (i.e. creating sales orders (or rejections). Opportunity refers to the possibility for a business to offer products on the basis of the customer’s desire. For example, if a person is interested in a particular product during an event or sale the interest is seen as a chance to do business with the client.
The sales process can be tracked and evaluated more effectively with the aid in opportunity Management because it contains the sales process that guides the business to follow specific best practices for sales. It can be altered or altered based on the requirements of the company. Opportunity Management is generally used in longer sales cycles, and when there are large prices.
Sales contract
The sales agreement is an arrangement to offer an item to the buyer with a set price or discount, based on the amount or value for a specified time. Once the period of validity is over and the contract ceases to be longer valid to sell the product at the price agreed upon. Management of contracts increases customer loyalty and retention by offering cheaper prices than typical costs.
Quotations
An agreement (often legally binding) between a buyer and the company for a particular product that has a cost and for a specific duration.Quotations are converted into the sales order or may be copied and used to create another quotation. Management of quotes improves customer relations and assists companies in offering price points that are competitive for a specific time. The period of validity for quotes is generally shorter than the duration of contracts in the management of contracts.
Sales Order Management
The term “sales order” refers to a sale or purchase is a request by a consumer to an organisation to purchase specific goods and then have them delivered on the date requested. The sales order is the sale transaction that is monitored to determine the amount of revenue earned by the business. It could be made with references to quotations or contracts. Customers are happy if they can choose from a variety of buying choices. If the item ordered isn’t in stock at the time requested An organization must be able to provide substitutes to satisfy the needs of the client. Sales transaction functions support the confirmation of customer orders and management of order status, cross-sells, up-sells, product substitution, and many more.
Analytical sales
Sales analytics provides companies with the ability to see the entire selling cycle from a reporting perspective. It provides the lifecycle of a customer that helps companies take crucial decisions when it comes to making changes to their business processes. It can also help determine the buying habits of customers. It also assists organizations in focusing on the most important customers and ensuring that they receive timely service. Sales analytics cover all SAP functions of CRM from a standpoint of reporting including sales analytics, marketing analysis, analytics for service as well as IC analytics
SAP CRM Service
The SAP CRM service equips professionals with the skills and resources they need to operate a service business effectively and efficiently within the service industry. From answering the initial inquiry, producing a quote, processing it, making orders, appointing the best presentation to the field service, all the way through confirmation and charging the client for the services rendered.Key capability Service includes the following scenarios: Case Management.
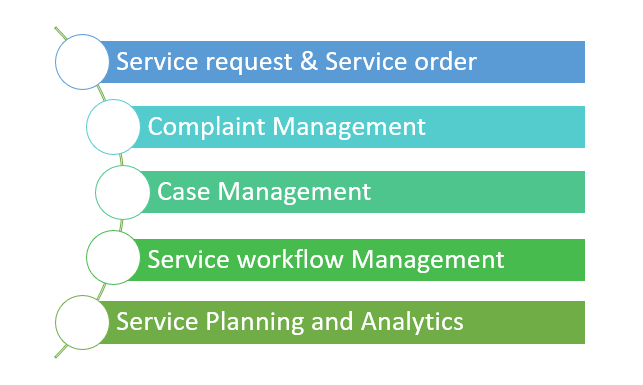
- Complaints and Returns Management
- In-House Repair
- Recall Management
- New and Changed Service Parts, Reverse Logistic
- Service Contract and Entitlement Management
- Service Order Management
- Service Order Management for Planned Services
- Service Order Management with ERP Billing
- Services Order Management with External Resource Procurement
- Service Order Management using Service Part Procurement
- Usage-Based Service Contract Management
Complaints and Returns Management
You can use this scenario to manage customer complaints in your service and sales organizations. A complaint is a statement of dissatisfaction a client can express regardinga product or service. If a consumer returns a product without filing a complaint, it is considered a return. The complaints management system you employ in your organization describes the entire process of complaints beginning with the filing of a complaint, the analysis of the technical aspect and the following-up steps, all the way to statistical analysis.
In-House Repair
The business scenario is used to manage the entire internal repair process in your facility, from creating the repair request to the billing.The In-House Repair scenario consists of
- Order Management and Order Processing
- Logistics Integration
- Controlling Integration
- Escalation Management
- Analysis
Recall Management
Service parts suppliers can use this scenario to handle recalls for defective parts (service parts) that remain in their warehouse inventory for customers. This scenario covers, among other things, the complaints processing process that is a way to make complaints, as well as complaints referring to invoice documents, returns and repair orders for in-house repairs for services, products, or delivery services which customers are unhappy with. The complaints can be related to products or not referred to products. The complaints based on the billing document, returns or repair orders in-house always refer to a particular product.
New and Changed Service Parts, Reverse Logistic
You can use this scenario to illustrate the complete procedure for complaints regarding service parts and other parts used in your business, including using analytical techniques to produce returns, the proper procedures for follow-up, and statistical analyses.
- Returns are created when you solicit clients (merchants) for parts from service or if customers (merchants) are looking to return items, for instance, to decrease the number of parts that are not being used are stored in your warehouse. So, manufacturers can allow their customers to be more accommodating by allowing them to return items not sold in the quantity they had hoped for.
- You make used parts returns when customers return old parts to which they’ve already made an initial deposit. When buyers (merchants) return these items to the manufacturers, they get back the deposit they made at the time of purchase. In accordance with the state of the item returned, used parts are remanufactured.
- Concerns about invoices could result in a return. When you file these complaints, there’s a problem with an invoice. These complaints typically result in credit/debit memos like invoice corrections and even physical returns.
Service Contract Management
Service contracts have been negotiated with the customer Warranties, which were assigned items, base components installed or even individual objects. Long-term agreements between customers and businesses are called service contracts. There are service agreements in place.
In contracts, the buyer can be assured of services within a specified tolerance limit for a specific quantity,, such as, in a timeframe. The guaranteed services are represented through services, like hotline or maintenance services, which are defined in a particular contract item. The specific characteristics of service products are specified by Service Level Agreements (SLA),that is later verified by various parameters, like response time and availability time.
The parameters serve to describe the SLAs and be used to manage the processing process.
Warranty rights can be easily allocated to specific products, installed base components,, or even specific objects. When you create service orders or confirmations, repair orders or complaints and complaints, the system checks the background to determine if there is a warranty and assigns it accordingly. When calculating the cost of parts and services in the billing process, warranties can be considered with the help of appropriate discounts.
Service Order Management
This business scenario identifies the procedures that are essential to the provision of services, beginning with the process of processing the service order quote and the subsequent processing of the actual order from the initial quote to the billing and other analysis.
Service Order Management for Planned Services
This business scenario is used to plan ahead and arrange services scheduled to occur at certain times, like maintenance or quote creation.Service plans can help you cut costs caused by unexpected downtimes and boost efficiency, for instance, through more clear and streamlined scheduling, as well as effective scheduling of your resources, for example, employees or material.
Within the service plan, the scope of regular services is defined, and the due dates for services are determined and monitored. The simulation of the service plan gives you a list of future service orders. It also lets you determine how many resource requirements (service employees, service components) are are required for each order and the amount of work required for a specific time.
Service Order Management using ERP Billing
The Service order management scenario in business identifies the procedures that are essential to the delivery of services. This starts with processing an order for service and executing the actual order, from quotation to the billing process and various analyses. In this business scenario variation, you can set up the transfer of billing information in SAP ERP Central Component (SAP ECC) accounting, in which the data is processed and then posted.
Service Order Management with External Resource Procurement
Service ordering business model to identify the procedures that are essential to the delivery of the services, beginning with the process of processing the service order quote and the execution of the actual service request, all the way to billing and other analysis. This variant in the commercial scenario plans the outsourcing of external services that are planned for service orders and in-house repair orders.
Service Order Management with Service Part Procurement
Service orders management scenario to identify the steps crucial to the delivery of the services, beginning with the preparation of the service order quote and the execution of the actual service order all the way to billing and other analysis. This scenario variant allows businesses to procureof service components used in service orders or repairs in-house.
Usage-Based Service Contract Management
It is possible to use this business model to charge your clients services that have the specified usage amount (of the number of copies, for instance) once you’ve established the terms of a service contract. The options available allow you to visualize the entire business process, which includes the creation of a quotation for services and a contract in addition to the amount of usage by using counters and readings, as well as billing. SAP CRM can be described as the top system to process contracts and quotations, recording readings and managing the bill.
SAP CRM features and functions
SAP CRM is Parts of business suite to manage customer relationship .Although it would be impossible to discuss all of SAP CRM’s features in one article, we will focus on a few key ones that are essential for every organisation.
Interaction Center
The Interaction Center (IC) is an integral SAP CRM program that provides connectivity for businesses to their customers via multiple channels that are a part of SAP CRM capabilities (for these functions, it is referred to in the following terms: IC Marketing, IC Sales as well as IC Service).
Let’s say a customer contact an agent to make a an order for the first time or to voice complaints about a product that he purchased. The IC tool is able to handle customer complaints and helps the agent and the manager in communication. IC permits the agent to manage both outbound or outbound communications channels including fax, phone and email, chat and more.
IC functions is broken down into the following blocks that include telesales, telemarketing, customer service along with IC Management. This Email Response Management Service (ERMS) allows organizations to track customer email messages and respond to them promptly, while not going over the SLA.
Partner Channel Management
Partner Channel Management provides the capability for companies to collaborate more effectively with all the partners involved in the sales of their products. Partner Channel Management helps organizations to deepen their understanding of the business sustainability of their channel partners and comprehend their growth. This helps companies create their plans based on channel sales, maximizing growth while cutting down on overall manufacturing costs.
Web Channel
This Web Channel application provides the capability to use internet-based technologies to conduct sales and services, as well as conduct interactions with customers. SAP E-Commerce turns the web into a lucrative selling and interactivity channel. It can be used to support the B2B and B2C scenarios in business. It allows businesses to conduct their business without any involvement from a manual source. Customers can easily order and begin services via their Web Channel, which results in fewer errors on orders and reduces calls to customer service call centers. The channel is easy and simple to use accessible 24/7 and allows customers to access information about products from anywhere and at any time.
WebClient’s UI
The WebClient User Interface (WebClient User Interface) is a multi-functional business tool and lets you connect to transactions in a short amount of time by scrolling through different screen or transaction.
Remember the classic method of accessing various transaction types in SAP systems: using The Graphical User Interface (GUI) that requires users to enter various transaction codes to access the transactions. The process of remembering and accessing transaction codes is a hassle. To address this, SAP introduced WebClient UI in conjunction with SAP CRM 2006’s. This web UI lets individuals or different roles in an organisation to access and navigate various transactions with ease without having to remember the transaction code. Its WebClient UI is a role-based UI specifically designed for business users who have different tasks like SAP CRM Marketing, SAP CRM Sales, SAP CRM Service and IC. SAP has given management roles for all of the SAP CRM CRM core areas. It allows managers to access the needed data to improve their processes and serve their customers in a timely manner.
Based on the requirements for business, you can define the business roles for the workplace that your customer support representative will work in on a daily basis.
Mobile Solutions
A lot of customers have mobile employees “out on the road,” traveling to satisfy the needs of their customers. In the majority of cases the mobile employees don’t have the right devices and infrastructure that gives them with accurate information about business transactions or any other customer data. To meet this need for business, SAP CRM Mobile provides mobile capabilities that can help businesses solve these problems. For instance the sales and service information is offered that covers the majority of the important transactions and data required for technicians and sales professionals. Field employees can perform their tasks more efficiently. They won’t have to keep track of what they’ve discussed with a customer since they can connect to the internet and view interactions. As a result, less data is redundant.
Analytics
SAP CRM Analytics helps measure how well you can predict and improve customer relations. Through SAP CRM Analytics the information collected within the operations SAP CRM is examined by analyzing how customers are served. This could mean analyzing the segmentation of customers or identifying cross-selling or opportunities to upsell. SAP CRM Analytics helps forecast the needs of an organization and also determine the behavior of customers. Analysis and collection of data is a continuous and ongoing process that aids companies in planning customer interactions.
SAP CRM covers analytics that relate to customer information and interaction. Likewise, SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence (SAP BusinessObjects BI) provides a full set of reporting capabilities as a separate application software. SAP CRM Analytics provides the closed loop process, which is run to satisfy customers and builds loyalty among customers.
Case Study: Coca-Cola and SAP CRM
Coca-Cola, a global brand with over 200 product lines, implemented SAP CRM to manage customer relationships across various markets and cultures. The CRM system helped the company stay connected to customers, streamline processes, and improve profitability. Today, Coca-Cola spends 10% of its revenue on advertising and marketing, generating approximately $4 billion annually. SAP CRM has transformed Coca-Cola’s approach to customer relationship management, leading to improved customer satisfaction, increased sales efficiency, enhanced marketing effectiveness, and better service delivery.
Conclusion
SAP CRM is a game-changer for businesses in the digital age, streamlining sales processes, delivering personalized marketing campaigns, and providing top-notch customer service. It enhances operational efficiency, drives customer satisfaction, and provides a unified view of the customer. Its flexibility allows for seamless integration with other systems, enabling informed decisions and a consistent customer experience. Case studies from Coca-Cola demonstrate its transformative potential. SAP CRM is a strategic investment for sustainable growth and success.
What is SAP Business Suite
SAP Business Suite SAP Business Suite is a set of business software that facilitates the integration of data as well as processes. It also provides collaboration particular functions that are specific to the industry and capacity for reliability.SAP Business Suite is based on SAP’s technology platform, called Net Weaver.SAP Business Suite 7 application offers a synchronized release calendar for all components and applications throughout the suite.
Which is better SAP or Salesforce?
In the CRM industry, SAP CRM and Salesforce are both well-known, but there are some important differences in terms of pricing, user experience, and integrations. In terms of customer preference, Salesforce is in a superior position.
How does SAP CRM integrate with other systems?
SAP CRM offers a seamless customer relationship management experience by integrating with both SAP and non-SAP systems. It provides real-time master data synchronization, bi-directional options for accounts and contacts, and external pricing leveraged from SAP S/4HANA. SAP CRM can also be integrated with leading accounting software like Oracle, QuickBooks, Sage, and Microsoft Dynamics, as well as third-party data hygiene tools and marketing applications. The goal is to streamline operations, improve customer management, and enhance the overall customer experience by enabling better organization and data sharing across the entire business.
You might also like the below articles.
- Debugging for functional consultants
- SAP BRIM
- SAP ALM
- Cloud computing
- Advantages of sap
- SAP Solution Manager 7.2
- SAP Technical
- SAP Solution manager
- SAP C4HANA
- SAP Successfactors
- MRP live
- Inventory management
- SAP Best Practices
- Sap learning hub
Here are some interesting training videos you can watch on YouTube.