This blog post explores the fundamental elements and sub-elements of SAP security, an essential element in the administration and safeguarding of a SAP system. Its purpose is to maintain system integrity and ensure the protection of sensitive data.
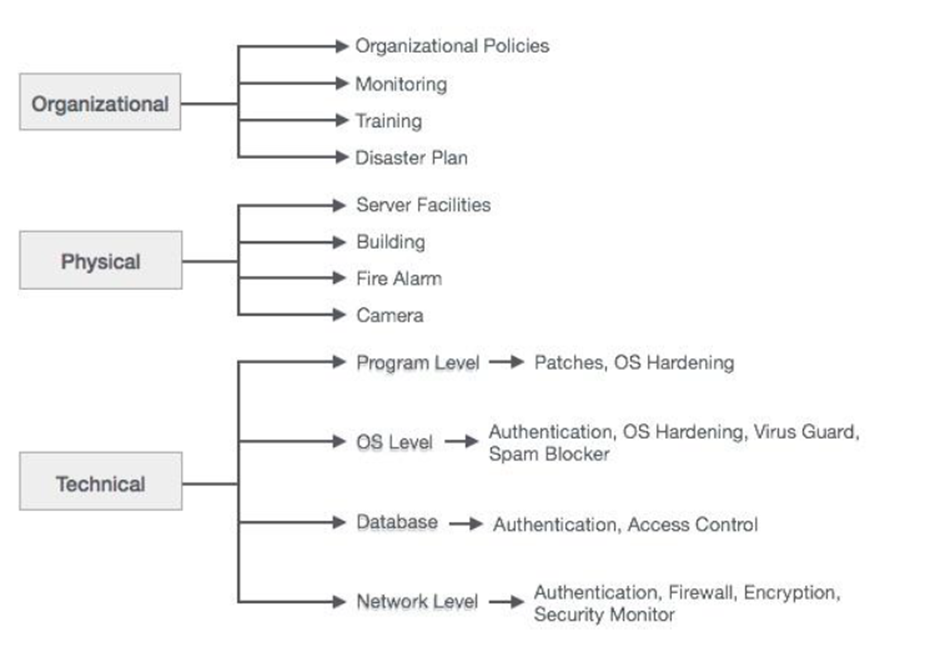
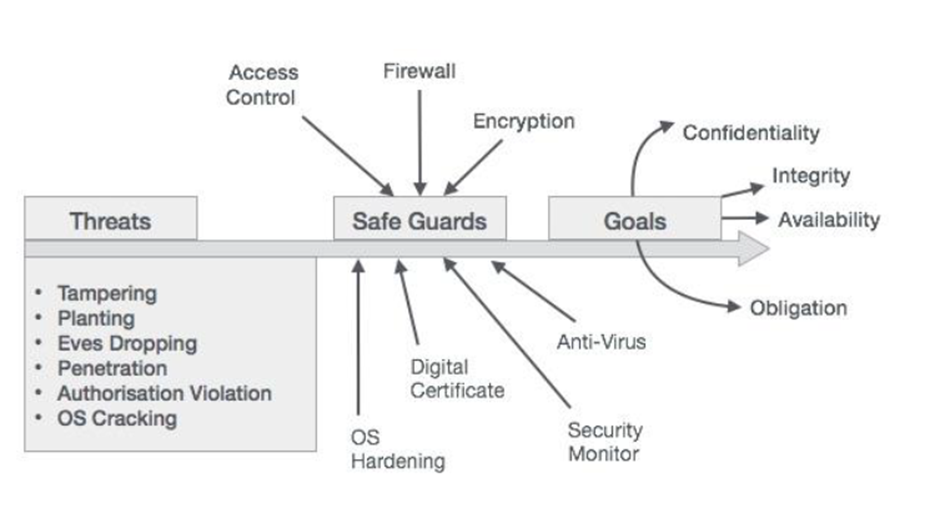
In order to safeguard user accounts, SAP runtime configurations grant them role-specific permissions to execute particular operations. Authorizations in SAP govern access to business process activities and transactions. A robust system incorporates security measures such as access control, firewalls, encryption, operating system hardening, digital certificates, security monitors, and antivirus to prevent the loss or harm of data. These protocols guarantee the protection of information and thwart unauthorized entry.
Table of Contents
What is SAP Security?
Implementing network communications measures, safeguarding against failed logins, managing passwords, establishing security policies, examining passwords, ensuring database security, setting up security policies, and contemplating a single sign-on for SAP System Security are all components of SAP Security.
SAP mandates the adoption of security protocols to safeguard its systems and sensitive data against unauthorized intrusion within a distributed environment. Authentication methods, database security, network and communication security, and the protection of standard users are among these measures. Preventing unauthorized access and human error requires that profile policies and system security policies be consistently monitored and maintained. Preventing unauthorized access to the system requires provisioning, as well as the consistent enforcement and evaluation of these policies.
In order to guarantee the security of a system, a thorough comprehension of user access profiles, password policies, data encryption, and authorization techniques is imperative. It is advisable to conduct routine assessments of the SAP System Landscape and closely monitor any modifications made to access profiles and configuration.
Ensuring the safeguarding of standard superusers and prudent configuration of user profile attributes and values are imperative in order to fulfill system security obligations. It is critical to have a comprehensive comprehension of the network’s architecture and to activate network services only after conducting exhaustive testing prior to communicating over a network. For data transmitted over a network to be protected, private keys are necessary.
Security Importance in Distributed Environments
- Potential leaks of critical information and data due to a lack of password policies and poorly maintained standard superusers.
- Key reasons for system security breaches include:
- Inadequate password maintenance.
- Poor maintenance of standard, super, and DB users.
- incorrect definition of profile parameters.
- inadequate monitoring of unsuccessful logon attempts and idle user session end policies.
- inadequate network communication security during data transmission over the internet.
- Poor maintenance of database users and lack of security measures.
- inadequate configuration and maintenance of single sign-on in a SAP environment.
Components of SAP Security
SAP Security is a comprehensive system that includes three main components:
- Authorization Management (BC-SEC-AUT): The BC-SEC-AUT sub-module manages user roles, authorizations, and permissions within the SAP system, ensuring access to only necessary functions and data.
- System Audit Information System (BC-SEC-AIS): The System Audit Information System (BC-SEC-AIS) monitors system activities, providing tools to track user actions, detect security breaches, and generate audit logs for compliance purposes.
- Security (BC-SEC):The core security component (BC-SEC) includes features like user authentication, password policies, and encryption mechanisms, as well as secure communication between SAP systems and external components.
SAP uses basic security tools such as firewalls, network ports, and SAP Router, which act as a proxy server to control access to SAP systems from external networks. Best practices for SAP Security include strong authentication methods like Single Sign-On (SSO), role-based access control (RBAC), and Transport Layer Security (TLS). Regular security audits are conducted to identify vulnerabilities, assess risks, and address gaps. Patch management ensures that SAP systems are up-to-date by applying security patches and updates, often addressing vulnerabilities.
SAP SECURITY: What it’s for
SAP system security is essential in a distributed environment; you must ensure that your data and processes satisfy the requirements of your organization without unauthorized access to sensitive information. Significant data loss can occur due to errors, inattentiveness, or unauthorized modifications made to the SAP system.
An unauthorized user can easily gain access to the SAP system if they are able to alter settings and key policies while logging in as a known approved user. Individuals who are granted access to a system are able to view its critical data and information. Additionally, that individual has access to other vital data and information. To ensure the confidentiality, availability, and integrity of a user system, this improves the functionality of secure authentication.
Application Security in SAP
SAP Security Overview
- SAP Systems stores sensitive customer and business data, necessitating regular audits for data safety and accuracy.
- Security checks are implemented to prevent unauthorized access to data and programs.
SAP Security Concepts
- STAD Data Transaction Numbers (STAD): Used to monitor, study, and support security ideas.
- SAP Cryptographic Library: The default encryption tool.
- Secure Network Communication (SNC): Used to connect different parts of a SAP system.
- Internet Transaction Server (ITS): Software designed to make SAP system applications accessible from a web browser.
- Networks Work (SAP Router, Firewalls, DMZ, Network Ports): Firewalls, DMZ, Network Ports, and SAP Router are basic security tools.
- Security for Web AS (Load Balancing, SSL, Enterprise Portal Security): SSL is a standard security method for creating secure connections between a server and a client.
- Single Sign-On: Allows users to log in to various SAP systems using the same user credentials.
- AIS (System for Audit Information): A tool for monitoring SAP system security.
Features of SAP Security for Mobile Apps
- Increased mobile usage of SAP apps increases vulnerability.
- Employees could lose important customer information.
- Most mobile devices can be wiped
- Popular mobile SAP security providers include SAP Afaria,
- SAP Net weaver Gateway, SAP Mobile Academy, and SAP Hana cloud.
What is GRC?
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) in the context of SAP
SAP GRC is a crucial tool for SAP security, ensuring data security and authorization standards. It comprises four modules: access control, process control, risk management, GTS (global trade services), and NFE (nota fiscal electronica). Access control is a key focus of SAP GRC, which includes access risk analysis (ARA), emergency access management (EAM), business role management (BRM), and access Request management (ARM). ARA focuses on the Segregation of Duties rule, while EAM provides ad hoc user access within the SAP System. BRM adopts a role-based approach, enabling the creation of new business roles accessible uniformly across different systems. ARM employs MSMP workflow principles to establish access request workflows.
The Fundamentals of SAP Security (Security vs GRC)
SAP security and governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) are distinct concepts conducts user access audits to identify issues related to user privileges and behavior. It then develops a compliant provisioning program, which is implemented using SAP security tools.
Can you explain SAP cybersecurity?
Due to the growing importance of SAP systems in financial planning and execution, SAP cybersecurity is an essential part of SAP system management and protection. There are two main kinds of cyberattacks: data theft and denial of service (DoS). Application blocking, file encryption, and database breach are all possible outcomes of attacks on SAP systems, which in turn impact SAP environments and HANA databases. Snooping on businesses, penetrating international networks, and obtaining vital information and procedures are all goals of Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs). Secure software, on-premises and private cloud apps, and configuration parameters all fall under SAP’s purview when it comes to security. With these issues resolved, SAP can guarantee the safety of cloud applications and software delivered to clients.
SAP security is an ongoing process, requiring regular assessments, user training, and collaboration between security teams to maintain a secure SAP environment. Regular assessments, user training, and collaboration between security teams are essential for ensuring the safeguarding of data, adherence to authorization protocols, and effective risk mitigation.
You might also like the below articles.
- Comprehensive guide to go live
- SAP EHS Module
- Power of generative ai in sap
- SAP Joule Comprehensive Guide
- Mastering the dunning process sap
- Creation of chart of accounts in sap fico
- Different roles of an sap consultant
- understanding sap system landscape
- Product costing in sap
- Copa in sap
- subcontracting process in sap mm
- SAP S4hana cloud
- Disaster Recovery in SAP HANA Cloud
- SAP ABAP beginner’s journey
- Year-end activities in sap
- SAP Project system module
- SAP DMS
- SAP ECC vs SAP HANA
- SAP Qualtrics
- Advance ATP
- SAP Project Implementation
- Exploring sap competitors
- Procure to pay process
- Order to cash process
- SAP S4hana inventory management
- SAP CPQ
- S4hana cloud upgrade schedule
- SAP Lumira
- SAP Signavio
- OpenText vim
- SAP Commerce cloud
- SAP S/4HANA Data migration tools
- SAP CPI integration
- SAP GTS for International Businesses
- Rise with sap
- What is Hyperscalers
- SAP bpc comprehensive guide
- SAP Business One
- Production Planning