Table of Contents
Introduction to OData
OData (Open Data Protocol) is an open standard that enables external applications to connect and manipulate data from various sources using RESTful APIs. Within SAP, OData serves as a means to connect SAP system data and applications, making it easier than ever to retrieve data and integrate apps.
Why OData Matters in SAP
The adoption of Open Data Protocol within SAP systems brings numerous advantages. Here are some key points:
1. Reducing Development Effort
Open Data Protocol in sap abap makes it much easier to access SAP backend data by reducing the amount of work required. Developers can save time and money by utilizing a standardized mechanism to query and modify data.
2. Cost-Effective Solution
Open Data Protocol makes it much easier to access SAP backend data by reducing the amount of work required. Developers can save time and money by utilizing a standardized mechanism to query and modify data. Companies can save money using OData. By streamlining the data landscape and making it more straightforward to manage and expand, OData significantly reduces the integration costs of data.
3. Enhanced Scalability
Open Data Protocolin sap abap increases the scalability of SAP systems. Its standardized approach ensures that data access can grow with the organization’s needs, supporting both SAP and non-SAP applications.
4. Simplified Maintenance
Open Data Protocol in sap abap simplifies data maintenance tasks, resulting in lower maintenance costs and more effective overall system performance.
How does OData integrate with SAP Fiori and SAP S/4HANA?
SAP S/4HANA OData
The foundation for SAP Fiori, as well as SAP S/4HANA’s communication with other systems and among itself, is Open Data Protocol. The way in which the two platforms interact is as follows:
- Open Data Protocol within SAP Fiori enables the responsive, lightweight, and user-centric development of SAP Fiori applications.
- Data Binding: A Fiori application binds UI components to the backend databases in real time by using Open Data Protocol services.
- Annotations: The annotations are in OData format, and metadata (such as labels, transparency, and field groups) describe how elements of the user interface behave.
- Fiori Elements. These templates eliminate the need to write custom code by automatically generating user interfaces (UIs) built on OData Service metadata and annotations.
- Service Consumption: To facilitate smooth CRUD operations with SAP information, Fiori apps utilize Open Data Protocol services that are accessible via SAP Gateway.
Business objects and processes are exposed as APIs for integration and extension using OData in SAP S/4HANA.
- Standard APIs: Through the SAP API Business Hub, SAP offers hundreds of pre-built OData V2 APIs that cover various modules, including finance, sales, procurement, and more.
The middleware that enables the creation and use of OData services from the ABAP stack is SAP Gateway. - Service Activation: Using transactions such as /IWFND/MAINT_SERVICE and /IWFND/GW_CLIENT, developers can test and activate OData services.
Integration Scenarios: Third-party integrations (such as ServiceNow and Boomi) and side-by-side extensions are all made possible by OData APIs.

OData Components in SAP Environment
OData in the SAP environment utilizes several components:
- GW_CORE: OData Libraries
- IW_FND: Runtime Component, metadata store, Shared Services
- IW_BEP: Business Enablement Provisioning
- IW_HDB: Business content adaptor for SAP gateway with SAP HANA
Basic Concepts of OData in SAP
- CRUD Operations: These operations (create, read, update, and delete) are fundamental to handling data in an entity set.
- Entity Set: A container that includes a structure, DDIC table, or CDS view.
- Association: Defines relationships between two or more entity types.
- The Expand Query Option is used to retrieve data from both entity sets in a single request call.
- Media Handling: Manages media data such as PDFs, PNGs, files, and videos.
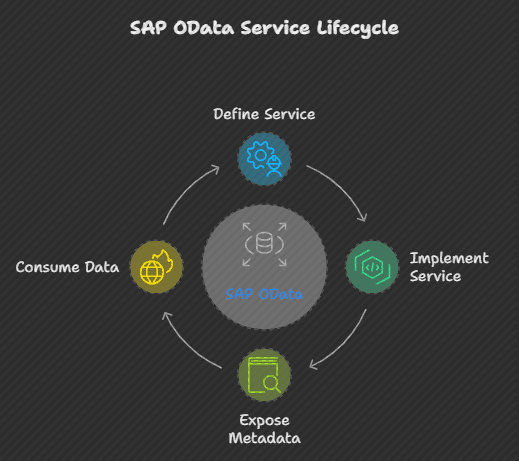
How to Make OData in SAP: A Step-by-Step Guide
To create OData services in SAP environment, follow these steps:
- Go to SEGW transaction code and create a project.
- Import DDIC structure or create a manual structure.
- Generate the structure.
- SAP will automatically create predefined classes and services.
- Add the service in the Service Maintenance transaction code.
- Please add the service according to the system name.
- To retrieve the necessary data, navigate to the Gateway Client and use the URI + GET syntax.
Conclusion
OData is a crucial tool in the SAP environment, simplifying and enhancing data integration and access. It provides a consistent method for accessing SAP backend data via RESTful APIs, making it easier to connect with SAP as well as non-SAP software. OData provides a flexible yet reliable interface for querying various data sources with identical formats, compatible with both web-based and mobile apps for optimal use. Best practices for developing and using RESTful APIs are also provided to ensure optimal results within and throughout its ecosystem. OData increases accessibility, as well as integration and overall effectiveness, for SAP ecosystem users alike.
You might also find the following articles interesting.
- learn sap btp
- Retail insights with sap car
- sap architecture a comprehensive guide
- leanix an introductory guide
- building side by side extensions on sap btp
- sap ecc vs s4 hana key changes and benefits
- sap ides
- Understanding rfno in sap s4hana
- SAP Clean Core
- SAP ABAP begnner’s journey
- Grow with sap vs rise with sap comparison
- Rise with sap
- Year-end activities in sap
- SAP TM Transaction codes
- ethical ai development
- sap migration data configuration tools
- simplifying sap s4hana custom code migration
- sap ewm integration
- sap project intelligence network
- advanced production integration with sap ewm
- Credit management comparison of sap fscm
- SAP EWM
- sap s4hana migration
- GST E invoice
- understanding abap objects
- SAP interfaces
- Joule ai copilot
- Mastering sap background job processing
- SAP Ewm tcodes a handy guide
- Object-oriented programming in sap abap
- understanding sap license costs
- SAP Datasphere
- industry4.0 with sap
- Condition contract management in sap s4 hana
- Comprehensive guide to go live
- SAP EHS Module
- Power of generative ai in sap
- SAP Joule Comprehensive Guide
- Mastering the dunning process sap
- Creation of chart of accounts in sap fico
- Different roles of an sap consultant
- understanding sap system landscape
- Product costing in sap
- Copa in sap
- subcontracting process in sap mm
- SAP S4hana cloud