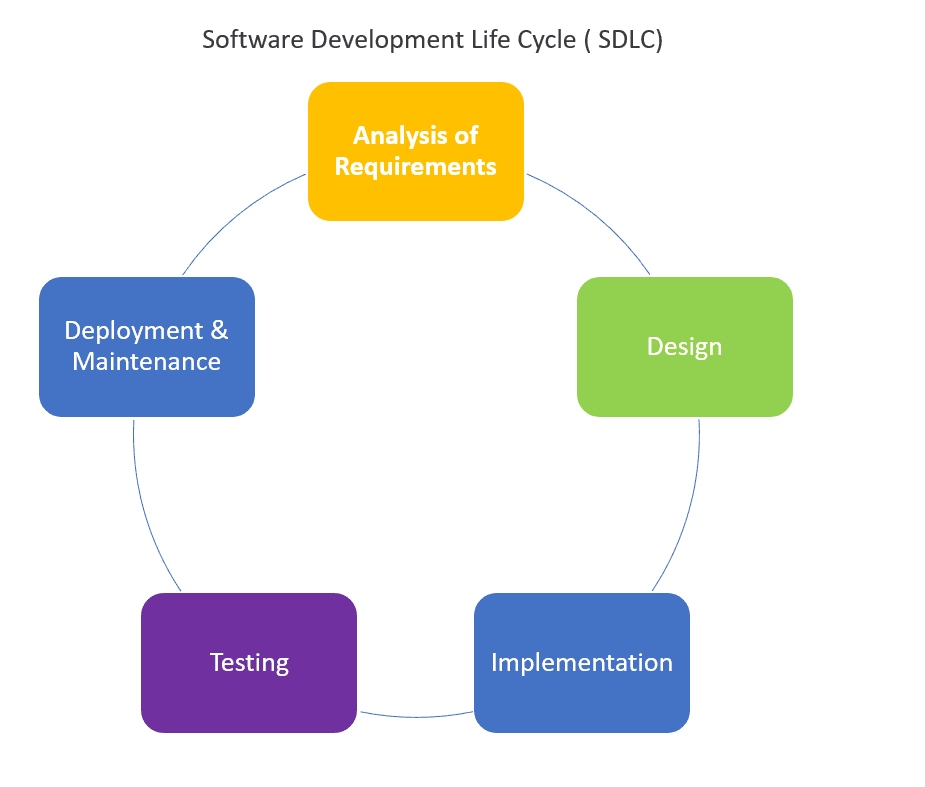
SDLC, meaning Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), is a software development process. It includes requirements gathering, design, development, testing, and maintenance. The software development life cycle is a process that includes stages like requirement gathering, design, development, testing, and maintenance.The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a comprehensive process used by software developers and project managers to design, develop, test, and deploy software applications. This structured approach helps ensure that the final product meets the client’s requirements and functions as intended. Here, we delve into the key phases of SDLC and explore their importance.
Software Engineering’s Software Development Life Cycle serves as our guide, leading us through the intricate process of producing robust and reliable software products. Let’s embark together on this adventure:
Table of Contents
What is SDLC
SDLC is a process for developing information systems through investigation, analysis, design, implementation, and maintenance. it is also known as the development of information systems or applications. It’s also known as the Waterfall Model. Several methodologies or models can be used to guide the life cycle of software development.
At its core, SDLC describes a structured process we take when designing, developing, testing, deploying and maintaining software applications. However, unlike its linear predecessor, it adapts dynamically based on project needs, team collaboration needs and ever-evolving requirements.
Some of these include the following:
- Linear or Waterfall Model
- Agile methodology
- Rapid Application Development (RAD)
- Joint Application Development (JAD)
- Prototype
The Software Development Life Cycle ( SDLC) is a process of formal, logical steps to develop a software product. The phases of SDLC may vary slightly but generally include the following:

What are the stages of SDLC?
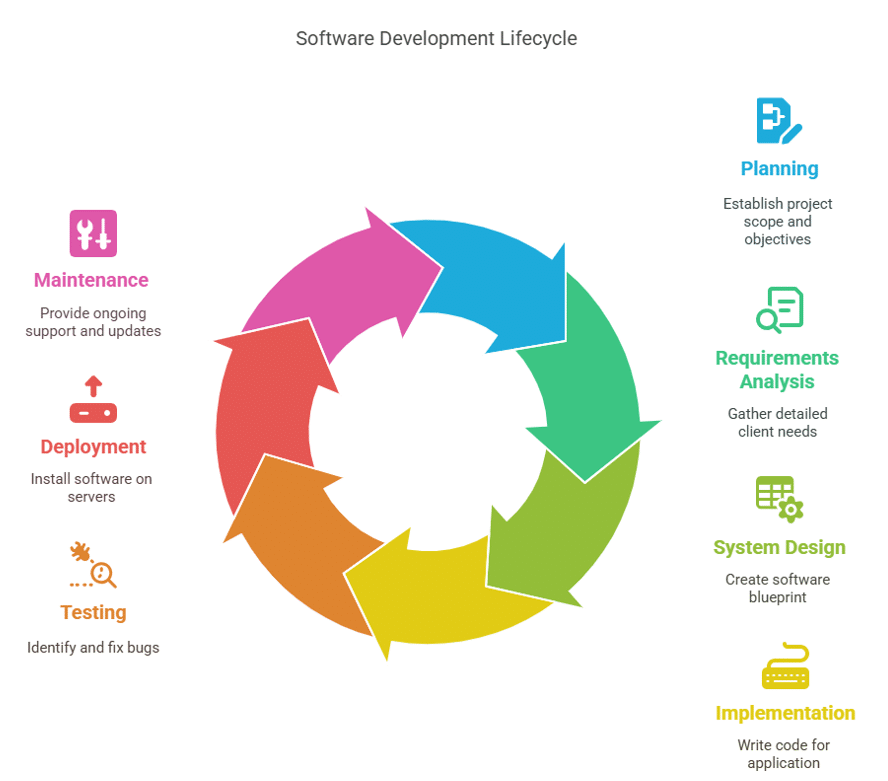
1. Planning
The planning phase involves establishing the project’s scope, objectives, and feasibility. During this stage, stakeholders and project managers collaborate to identify the project’s requirements, budget, and timeline. Effective planning sets the foundation for a successful software development project.
2. Requirements Analysis
In this phase, the development team gathers detailed information about the client’s needs and expectations. This involves communicating with end-users, stakeholders, and other relevant parties to create a comprehensive list of functional and non-functional requirements. Accurate requirements analysis is crucial for guiding the development process and avoiding misunderstandings.
3. System Design
The design phase involves creating a blueprint for the software application based on the requirements gathered. This includes defining the system architecture, selecting the technology stack, and outlining the user interface and user experience (UI/UX). A well-designed system ensures that the software is scalable, maintainable, and user-friendly.
4. Implementation (Coding)
During the implementation phase, developers write the actual code for the software application. This involves translating the design specifications into a functional program using the chosen programming languages and frameworks. Effective implementation requires skilled developers and adherence to coding standards and best practices.
5. Testing
In the testing phase, the software application undergoes rigorous testing to identify and fix any bugs or deficiencies. QA engineers perform various tests, including unit tests, integration tests, system tests, and user acceptance tests (UAT). Thorough testing ensures that the software is reliable, secure, and performs as expected.
6. Deployment
Once the software has been thoroughly tested, it is deployed to the production environment. This phase involves installing the software on the client’s servers, configuring the system, and performing any necessary data migration. Successful deployment ensures that the software is ready for use by end-users.
7. Maintenance
The maintenance phase involves providing ongoing support and updates for the software application. This includes fixing any issues that arise, implementing new features, and ensuring compatibility with evolving technologies. Regular maintenance helps extend the software’s lifespan and keeps it relevant to users’ needs.
Software Training and Support
A significant number of software projects fail because the developers don’t know how long a development team will take to build software if none of them end up using it. Occasionally people are resistant to change and fear is new, and as part of the deployment process, it is very important to have training classes for the most enthusiastic users of the software (build excitement and trust), shift training to neutral users in tandem with avid supporters, and finally incorporate the rest of the organization into their adoption. Users will have a lot of questions and problems with software
Maintenance Services
This may take much more time than the program’s initial creation to update and upgrade the software to deal with newly found issues or specifications. Not only can the code not match the original design, but it can only be essential for a software developer to decide how software functions after it is completed. Approximately 2/3 of all software work is maintenance, which can be misleading. A little error fixing is part of it. Hope these articles help to understand SDLC
Refer to the SDLC Documentation
Exploring SDLC Models
Waterfall SDLC Model Description:
The Waterfall model is a linear approach with benefits like simplicity, clear milestones, and well-defined phases. It requires thorough documentation for each stage, but rigidity and inflexible requirements may cause delays. Ideal for projects with clear requirements and scope.
Agile SDLC Model
Agile is a flexible, iterative development approach that breaks projects down into shorter sprints with frequent feedback loops. It offers advantages such as quick adaptation to evolving requirements, early feedback, and faster delivery. However, it requires active team collaboration, less emphasis on extensive documentation, and scope creep.
Iterative SDLC Model
Iterative models combine Waterfall and Agile approaches for software development life cycle management, allowing for incremental progress and early identification of issues. They are adaptable, but have drawbacks like long development timelines, complexity, coordination, and time consumption.
Spiral SDLC Model
The iterative software development approach involves multiple cycles of risk analysis, feedback, and evaluation, offering benefits like regular risk evaluation and adaptability to changing requirements, but also requiring experienced project management.
Conclusion
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a framework that guides software projects from concept to implementation, ensuring that the highest quality criteria are met on time and within budget. This blog looked at the various stages of the project, from initial planning and requirement gathering to coding testing, deployment, and maintenance.By following these structured phases, development teams can produce reliable, efficient, and user-friendly software that meets clients’ expectations. Understanding and implementing SDLC best practices is essential for successful software development projects.
Happy Learning ..!! Please check below tutorial links to learn more about the SAP Tutorials
- Available to Promise (ATP) in SAP
- Replenishment lead time (RLT)
- SAP Sales Integration with other Modules
- SD Advanced Pricing
- SAP S/4HANA
- User exit in sap
- SAP Fiori App
- SAP Fieldglass
- SAP Customer Engagement & Commerce Suite(CEC Suite)
- Hybris Marketing
- Third-Party Sales in SAP